Contents
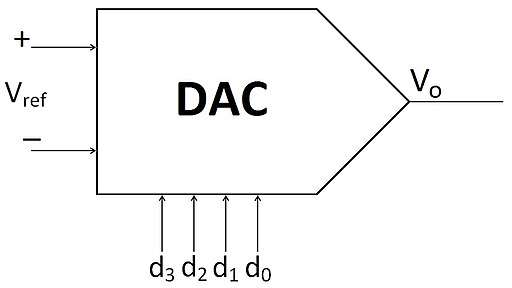
In this post we provide a tool that computes the analog output voltage from a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC). The DAC can have any number of bits associated with it.
Calculator
Enter the following:
- Reference voltage
- Number of Bits in the DAC (e.g. 8 or 12 bits)
- Digital Input (e.g. 10101)
The tool will provide the Analog Output value from the DAC
Example Calculation
8-bit DAC
For a reference voltage of 5 Volt, digital word 0101010 into an 8-bit DAC, the analog output voltage is 0.82 Volt. If the digital input is 11111111, the output is at the max value of 5 Volt.
12-bit DAC
For the same reference voltage of 5V, digital word 110101001111 into a 12-bit DAC gives an output voltage of 4.16 Volt.
A similar calculation can be applied to 4-bit, 10-bit DACs.
Remember to specify the bit depth of the DAC as that determines the voltage resolution.
Background
The output of a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) is an analog signal that corresponds to the digital input values it receives. A DAC takes digital data, usually in binary form, and converts it into a continuous analog signal. The nature of this analog output can vary depending on the specific application and the design of the DAC, but here are a couple of key considerations
Voltage or Current
- Voltage Output DACs: Many DACs produce a voltage output. The exact voltage level corresponds to the digital value input, scaled according to the DAC’s reference voltage and resolution. For example, in a system with a reference voltage of 5V and a DAC resolution of 8 bits, each step in the digital input results in a change of approximately 19.53 mV (5V/256) in the output voltage. Use this tool to calculate voltage resolution.
- Current Output DACs: Some DACs, especially those used in professional audio or precision applications, output a current instead of a voltage. The advantage of current output DACs lies in their ability to drive very high precision and low noise levels, particularly when used with current-to-voltage converters at the output stage.
